A supplier feedback loop is a continuous process of communication between a company and its suppliers, designed to gather valuable insights, address concerns, and drive mutual improvement. This iterative cycle is fundamental to modern supply chain management, as it enables organizations to identify areas for improvement in procurement processes, enhance product quality and delivery timelines, strengthen collaborative relationships with key suppliers, and drive innovation through shared knowledge and expertise. By establishing a robust feedback mechanism, companies can create a more responsive and agile supply chain that adapts to changing market conditions and customer demands.
| Key Takeaways |
|---|
| • A supplier feedback loop is crucial for improving supply chain efficiency and relationships |
| • Effective feedback loops involve collecting, analyzing, and acting on supplier insights |
| • Regular communication and transparency are essential for successful implementation |
| • Technology plays a vital role in streamlining the feedback process |
| • Overcoming challenges requires commitment and cross-departmental collaboration |
Implementing a supplier feedback loop is a critical strategy for organizations aiming to enhance their supply chain management and foster stronger relationships with their vendors. This systematic approach to gathering, analyzing, and acting upon supplier insights can lead to significant improvements in operational efficiency, product quality, and overall business performance.
Key Components of a Supplier Feedback Loop
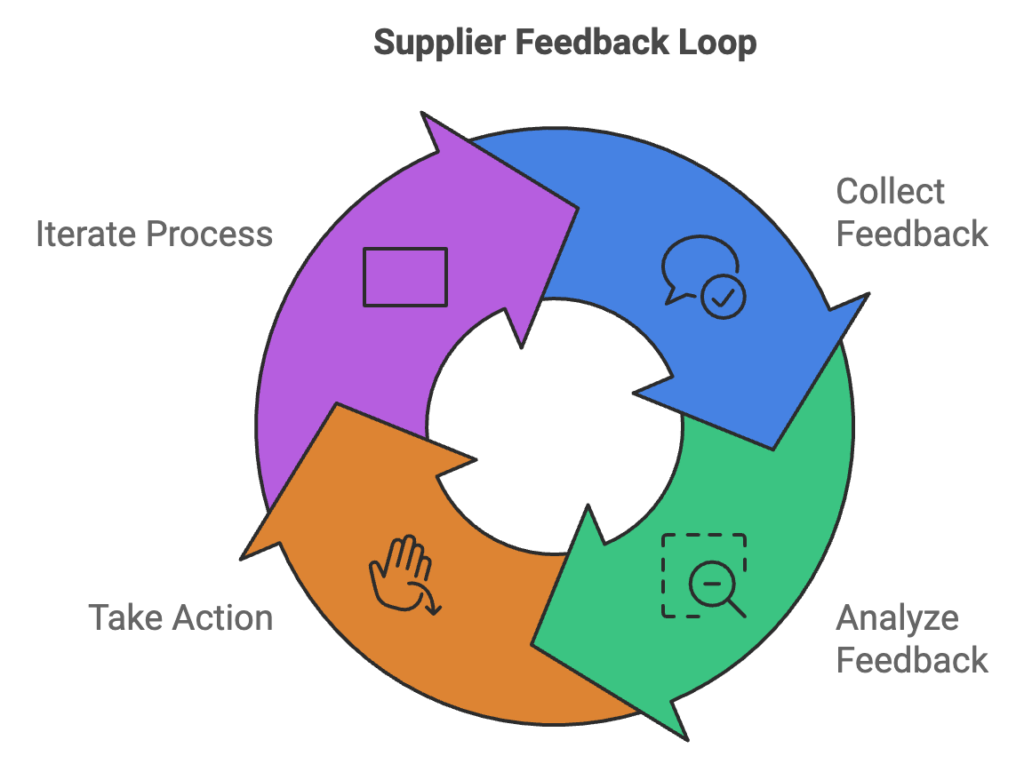
Collection of Feedback
The foundation of an effective supplier feedback loop is the systematic collection of information from suppliers. This process can be accomplished through various methods, including surveys, questionnaires, one-on-one interviews, and digital feedback platforms. Choosing the right channels for communication is crucial to encourage open and honest feedback from suppliers. A mix of digital and personal touchpoints often yields the most comprehensive results.
Analysis of Feedback
Once feedback is collected, it must be thoroughly analyzed to extract actionable insights. This stage involves data aggregation, performance benchmarking, and root cause analysis. Advanced analytics tools can significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of this process, allowing for more nuanced insights and predictive analysis.
Action Based on Feedback
The true value of a supplier feedback loop lies in the actions taken in response to the insights gained. This phase includes developing action plans, implementing process improvements, and providing supplier support. Transparency in this stage is crucial. Communicating the actions taken back to suppliers demonstrates a commitment to the feedback process and encourages ongoing participation.
Iteration of the Feedback Process
A successful supplier feedback loop is not a one-time event but an ongoing cycle of improvement. Regular iteration involves scheduling periodic reviews, refining the process, and tracking progress. This continuous approach ensures sustained improvement and adaptation to changing circumstances.
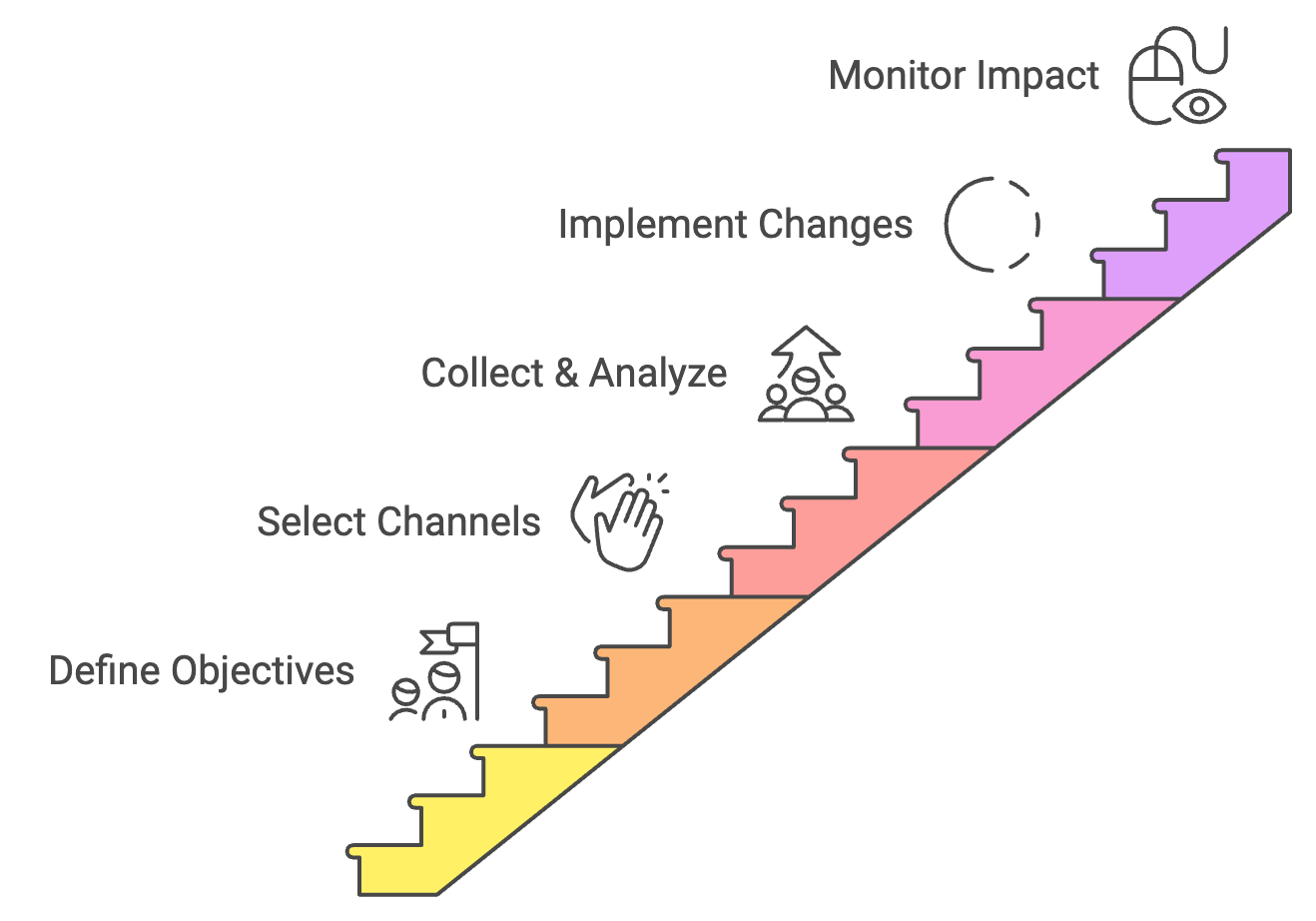
Steps to Implement a Supplier Feedback Loop
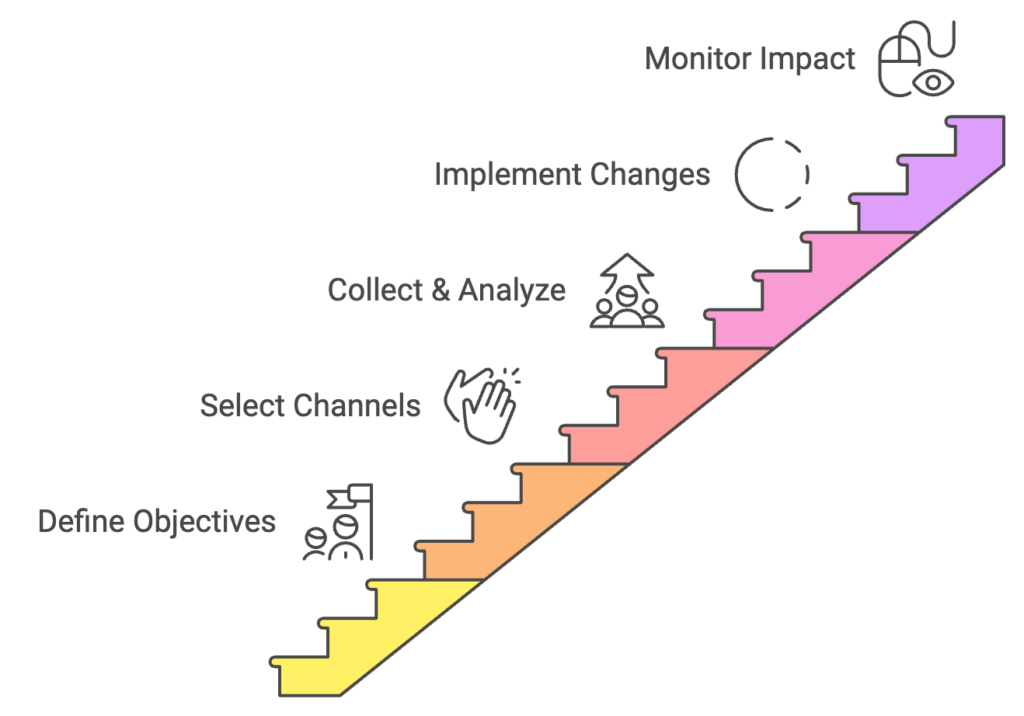
Define Objectives
Before launching a supplier feedback initiative, it’s essential to clearly define what the organization hopes to achieve. Objectives might include improving on-time delivery rates, enhancing product quality, reducing supply chain costs, or fostering innovation through supplier collaboration. These goals should align with broader business strategies and provide a clear direction for the feedback process.
Select Feedback Channels
Choosing the right tools and methods for feedback collection is crucial for ensuring high participation rates and quality input. Consider digital surveys, face-to-face meetings, and supplier portals. The selection of channels should take into account supplier preferences, technological capabilities, and the nature of the information being sought.
Collect and Analyze Feedback
When gathering supplier feedback, it’s important to ask clear, specific questions that align with defined objectives, provide a mix of quantitative and qualitative response options, and ensure anonymity when necessary to encourage honest feedback. For analysis, consider utilizing spend analysis tools to identify trends and patterns, conducting cross-functional reviews to gain diverse perspectives on the feedback, and prioritizing insights based on their potential impact and alignment with business goals.
Implement Changes and Monitor Impact
Turning feedback into action is where many organizations falter. To ensure success, develop clear action plans with assigned responsibilities and deadlines, communicate changes to both internal teams and suppliers, establish KPIs to measure the effectiveness of implemented changes, and regularly review progress and adjust strategies as needed.
Common Challenges in Implementing a Supplier Feedback Loop
Overcoming Resistance
Some suppliers may be hesitant to provide honest feedback, fearing potential negative consequences. To address this, clearly communicate the purpose and benefits of the feedback process, demonstrate a commitment to using feedback constructively, and recognize and reward suppliers for their participation and insights.
Managing Feedback Volume
As the feedback loop matures, organizations may find themselves inundated with data. To manage this effectively, implement data management systems to organize and prioritize feedback, use AI-driven analytics to identify critical insights quickly, and establish a triage system to address urgent issues promptly.
Balancing Feedback with Business Goals
While supplier feedback is valuable, it must be weighed against overall business objectives. This involves aligning feedback initiatives with strategic priorities, conducting cost-benefit analyses on proposed changes, and maintaining a long-term perspective when evaluating feedback-driven initiatives.
Best Practices for an Effective Supplier Feedback Loop
Consistency in Feedback Collection
Regular, predictable feedback intervals help maintain supplier engagement and provide timely insights. Consider establishing an annual feedback calendar, combining formal surveys with ongoing informal feedback mechanisms, and aligning feedback collection with key business cycles or events.
Cross-Department Collaboration
A successful supplier feedback loop requires input and buy-in from various stakeholders across the organization. Ensure that procurement, supply chain, and quality assurance teams are aligned on feedback objectives, cross-functional teams are involved in analyzing feedback and developing action plans, and executive leadership supports and champions the feedback initiative.
Closing the Feedback Loop
To maintain supplier trust and engagement, it’s crucial to demonstrate how their input is being used. Provide regular updates on actions taken in response to feedback, celebrate successes and improvements achieved through supplier collaboration, and seek ongoing input on the effectiveness of implemented changes.
Implementing a supplier feedback loop is a powerful strategy for organizations looking to enhance their supply chain performance and build stronger, more collaborative relationships with their vendors. By systematically collecting, analyzing, and acting on supplier insights, companies can drive continuous improvement, foster innovation, and create a more resilient and responsive supply chain ecosystem. As businesses continue to face complex global challenges, those that prioritize open communication and collaborative problem-solving with their suppliers will be best positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive marketplace.